ICT Lifecycle Management: Best Practices for Every Stage with eGRACS©
A step-by-step guide to managing ICT systems from planning and implementation to maintenance and retirement.
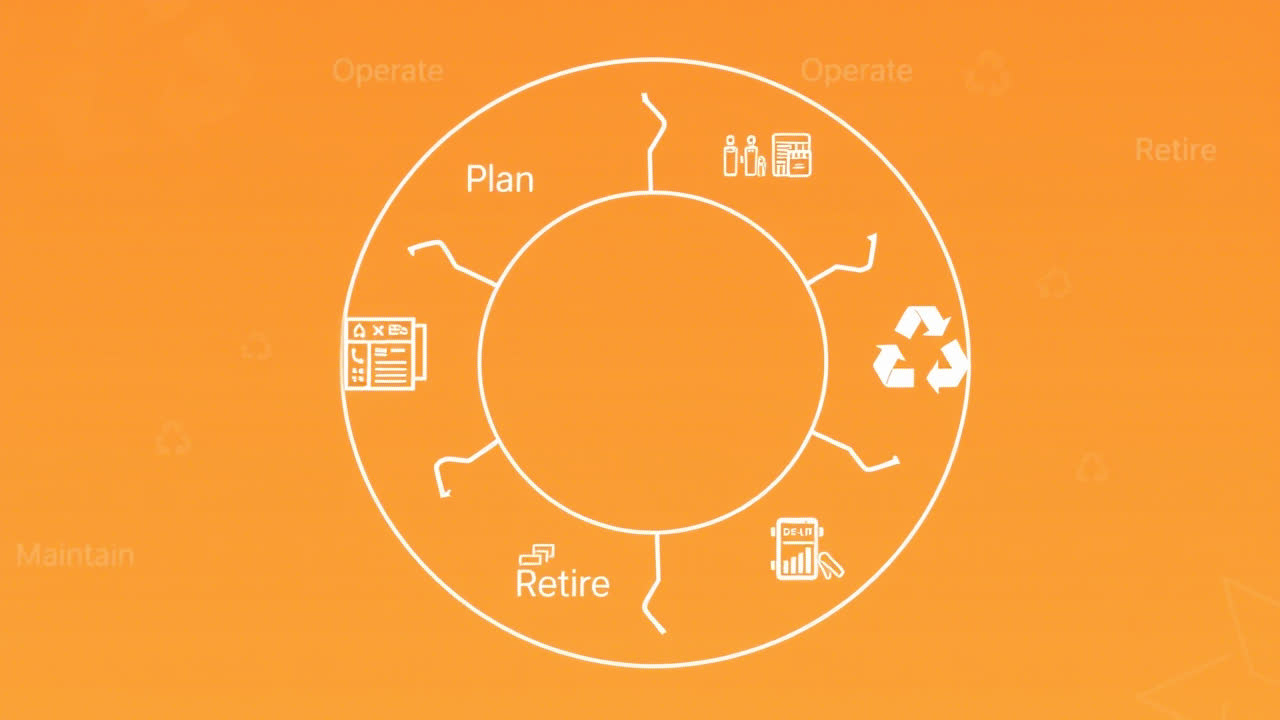 Managing ICT systems effectively requires more than just addressing immediate needs. It’s about ensuring each system serves its purpose efficiently throughout its lifecycle—from inception to retirement. The eGRACS framework provides a structured, best-practice approach for every stage, ensuring alignment with organisational goals while maintaining security and compliance.
Managing ICT systems effectively requires more than just addressing immediate needs. It’s about ensuring each system serves its purpose efficiently throughout its lifecycle—from inception to retirement. The eGRACS framework provides a structured, best-practice approach for every stage, ensuring alignment with organisational goals while maintaining security and compliance.
Stage 1: Planning Your ICT Systems
The planning stage is where everything begins. This is your chance to align technology solutions with business objectives, identify potential risks, and design systems that are scalable and secure.
Best Practices for Planning
- Define clear business objectives and align ICT goals accordingly.
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities early.
- Leverage eGRACS controls to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Stage 2: Implementing ICT Solutions
Implementation turns your plans into reality. It’s where systems are built, integrated, and deployed, ensuring they meet functional and security requirements.
Best Practices for Implementation
- Conduct rigorous testing at every step, from unit testing to user acceptance testing.
- Ensure systems are integrated seamlessly into your existing architecture.
- Use eGRACS governance practices to oversee deployment and minimise disruptions.
Stage 3: Operating ICT Systems
Once systems are live, their performance must be monitored and optimised. This stage focuses on ensuring reliability, security, and efficiency in daily operations.
Best Practices for Operation
- Establish robust monitoring systems to track performance and uptime.
- Use eGRACS controls to ensure operational compliance and risk mitigation.
- Regularly update and patch systems to protect against emerging threats.
Stage 4: Maintaining ICT Systems
Maintenance is about keeping systems running smoothly as business needs evolve. It involves continuous improvements and adapting to technological advancements.
Best Practices for Maintenance
- Schedule regular audits to identify and address inefficiencies.
- Document system updates and changes for transparency.
- Leverage eGRACS for structured change management processes.
Stage 5: Retiring ICT Systems
 All systems have a lifecycle, and retirement is the final stage. This involves securely decommissioning systems, migrating data, and minimising risks during the transition.
All systems have a lifecycle, and retirement is the final stage. This involves securely decommissioning systems, migrating data, and minimising risks during the transition.
Best Practices for Retirement
- Plan data migration to ensure no loss of critical information.
- Follow eGRACS security protocols for secure decommissioning.
- Recycle or dispose of hardware responsibly to maintain compliance.
The eGRACS Advantage in ICT Lifecycle Management
- End-to-End Control: Manage systems seamlessly across all stages of their lifecycle.
- Proactive Risk Management: Address potential risks before they become issues.
- Compliance Assurance: Maintain adherence to standards like GDPR and ISO 27001 throughout the lifecycle.
Who Should Use eGRACS?
eGRACS is designed for a diverse range of industries and organisations, including:
- Finance: Streamlines governance processes to meet strict regulatory standards.
- Healthcare: Protects patient data while ensuring HIPAA compliance.
- Retail: Aligns ICT operations across multiple locations for improved efficiency.
- Technology: Supports innovation while maintaining robust risk management practices.
Streamline Your ICT Lifecycle with eGRACS
From planning to retirement, eGRACS provides the tools and guidance needed for effective ICT lifecycle management. Take control of your systems today!