The Importance of Control Practices: Governance, Management, and Administration in eGRACS
Break down the three control practices and their critical roles in unified ICT governance.
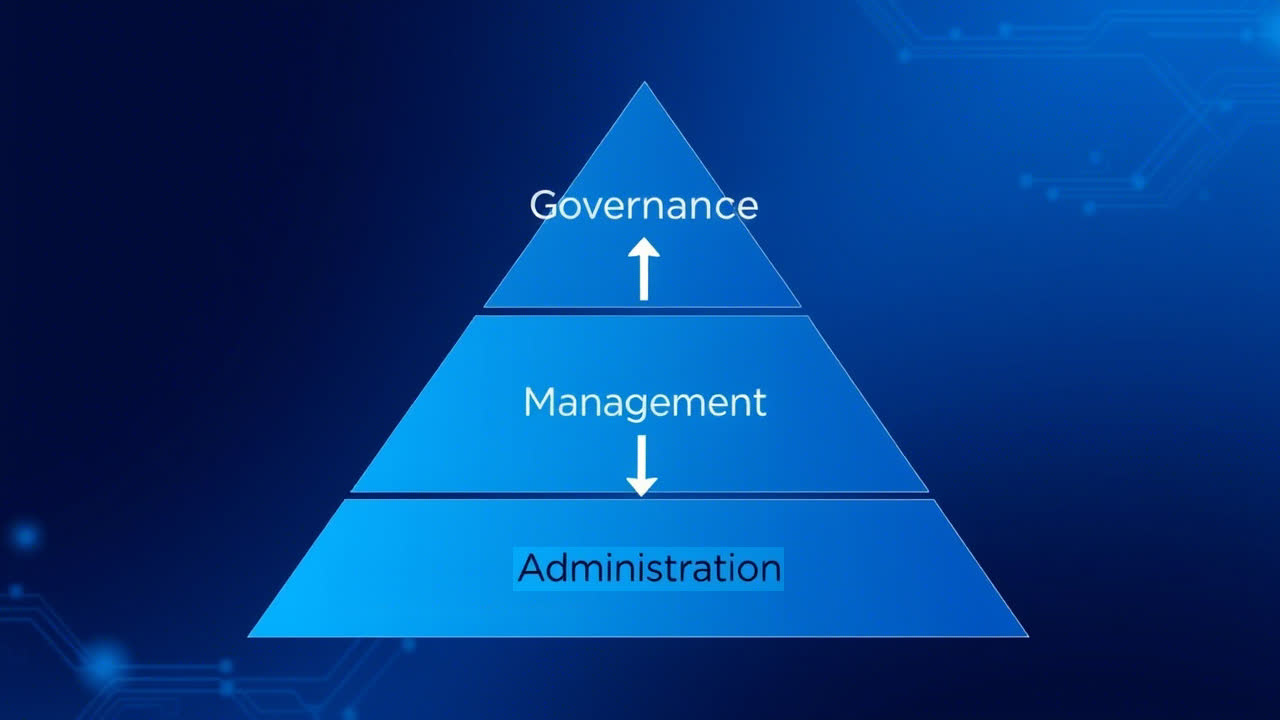 Effective ICT governance requires more than just frameworks and policies—it needs a structured approach that ensures clarity, collaboration, and accountability. The **eGRACS framework** achieves this through three critical control practices: Governance, Management, and Administration. Together, these practices form the backbone of unified ICT governance, creating a seamless flow from strategic decision-making to operational execution.
Effective ICT governance requires more than just frameworks and policies—it needs a structured approach that ensures clarity, collaboration, and accountability. The **eGRACS framework** achieves this through three critical control practices: Governance, Management, and Administration. Together, these practices form the backbone of unified ICT governance, creating a seamless flow from strategic decision-making to operational execution.
What Are Control Practices in eGRACS?
Control practices in eGRACS refer to structured processes and roles that ensure ICT systems are governed effectively at every level. They define how decisions are made, executed, and supported, providing a cohesive framework for managing complexity in ICT environments.
1. Governance: Setting the Strategic Direction
The Governance control practice focuses on high-level decision-making and strategic alignment. It ensures that ICT initiatives are fully integrated with organisational objectives and compliant with regulations.
Key Roles of Governance
- Defining Strategic Goals: Aligns ICT strategies with business priorities.
- Overseeing Risk and Compliance: Establishes policies to manage risks and meet regulatory requirements.
- Accountability: Ensures senior leadership takes responsibility for ICT outcomes.
2. Management: Bridging Strategy and Operations
Management serves as the link between governance and execution. It translates strategic goals into actionable plans, optimises resources, and oversees performance to ensure objectives are met effectively.
Key Roles of Management
- Resource Optimisation: Allocates resources to maximise efficiency and impact.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks progress against strategic goals and adjusts as needed.
- Team Leadership: Guides teams to execute ICT initiatives with precision and purpose.
3. Administration: Ensuring Seamless Execution
 The Administration control practice focuses on the day-to-day operations of ICT systems. It ensures that technical environments are maintained, systems are secure, and issues are resolved promptly to support business continuity.
The Administration control practice focuses on the day-to-day operations of ICT systems. It ensures that technical environments are maintained, systems are secure, and issues are resolved promptly to support business continuity.
Key Roles of Administration
- Operational Support: Handles system maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting.
- Security and Compliance: Enforces safeguards to protect data and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Technical Expertise: Ensures ICT infrastructure operates reliably and efficiently.
How Governance, Management, and Administration Work Together
Each control practice has a distinct role, but their true power lies in their collaboration. Governance sets the vision, Management develops the plan, and Administration ensures execution. This seamless interaction ensures that every aspect of ICT governance is aligned, efficient, and effective.
The Benefits of Control Practices in eGRACS
- Clarity and Accountability: Clearly defined roles ensure responsibilities are understood at every level.
- Strategic Alignment: Links ICT initiatives directly to organisational goals.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes and reduces redundancy across teams.
- Enhanced Security: Ensures consistent safeguards are applied throughout the ICT environment.
Who Should Use eGRACS?
eGRACS is designed for a diverse range of industries and organisations, including:
- Healthcare: Protects patient data while ensuring HIPAA compliance.
- Finance: Streamlines governance processes to meet strict regulatory standards.
- Retail: Aligns ICT operations across multiple locations for improved efficiency.
- Technology: Supports innovation while maintaining robust risk management practices.
Empower Your ICT Governance with eGRACS
The control practices of Governance, Management, and Administration form the foundation of effective ICT governance. With eGRACS, you can ensure these practices work together seamlessly to drive organisational success. Start your transformation today!